Clearwater Park Offsites Delivers Complex HDD Program Beneath Lake and Links
Nestled just east of Calgary, the growing city of Chestermere, Clearwater Park is a new master-planned, mixed-use community development.
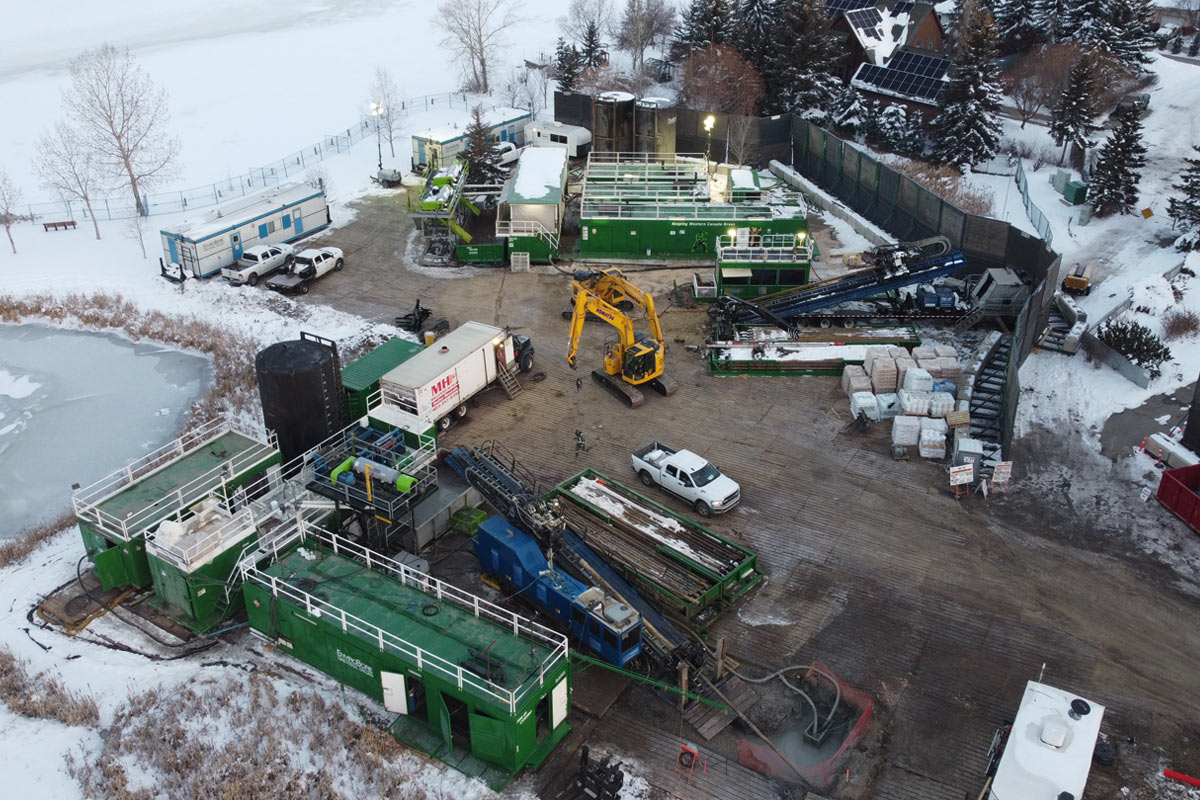
Situated on the shores of Lake Chestermere, the development requires extensive underground services. To meet tight alignment constraints and avoid disturbing the active summer lake community, the project team delivered more than 4,500 m of trenchless installations. These installations were done under roads, fairways, and even beneath Lake Chestermere itself.
With a combination of early contractor involvement, three different rigs, and multiple horizontal directional drilling (HDD) strategies, the project stands as a model for planning-intensive trenchless work in sensitive urban environments.
Project Scope and Timeline
Officially titled the Clearwater Park Offsites, the HDD program was executed to provide both water and sanitary service to the Clearwater Park development. The project was split into two phases due to seasonal constraints around the lake community.
Construction of the trenchless works began in March 2024. EnviroBore Directional Drilling mobilized its American Augers DD440T and DD240T rigs to a shared pad. The DD440 was tasked with crossing under Lake Chestermere, while the DD240 handled eastbound work beneath a major intersection. By early June 2024, six HDDs totaling 2,700 m were completed before operations paused for the summer. Work resumed in March 2025, concluding in mid-May, with seven additional bores totaling 2,325 m.
Team and Coordination
Led by Volker Stevin Canada as general contractor, with EnviroBore executing all HDD work, the project reached peak activity with 75 personnel onsite.
Bluefox Engineering, based in Calgary, Alberta, provided trenchless design and full construction supervision. They acted as the project’s dedicated trenchless engineering consultant.
Each organization maintained a dedicated project manager and onsite field office. This promoted seamless communication and rapid decision-making across the multi-bore operation.
Pipe & Bore Specifications
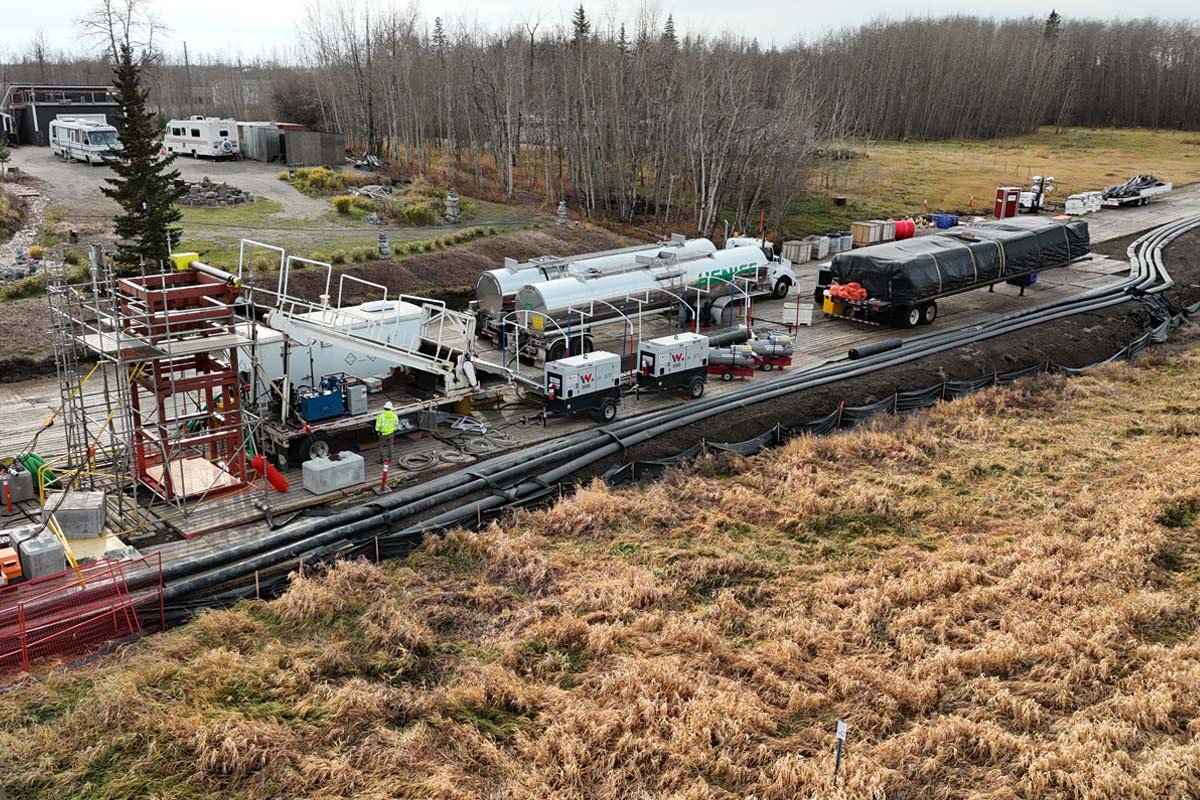
The project installed three sizes of DR11 HDPE pipe: 250 mm and 400 mm for the sanitary lines and 600 mm for the watermain.
The smaller two lines were installed side-by-side in a 36-in. reamed hole. Meanwhile, the 600-mm line was installed in its own 36-in. bore. Each bore followed a consistent reaming sequence: 12.25-in. pilot, followed by 24-, 30-, and final 36-in. reams. Individual bore lengths ranged from 350 to 700 m. In some cases, alignment separations were as tight as 2 m horizontally.

Rig Fleet and Segment Assignments
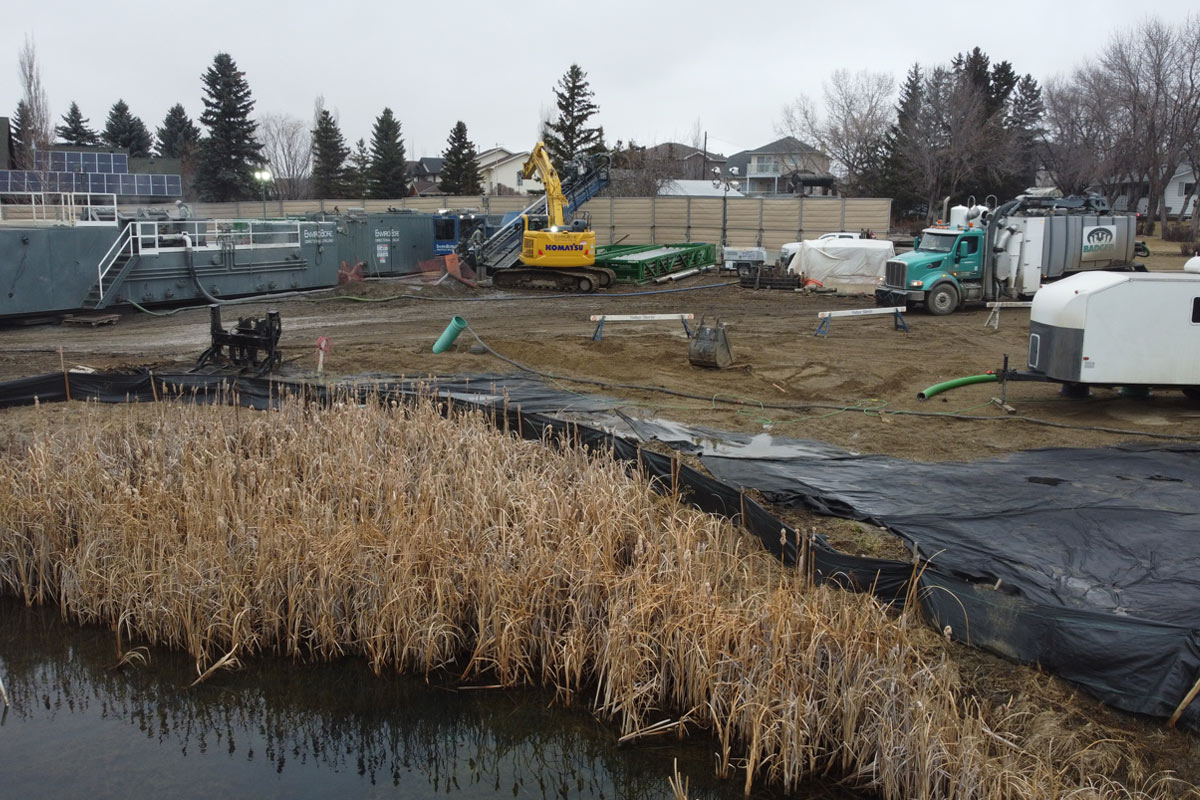
Completing the bores required three different HDD rigs: the DD440 for the Lake Chestermere bores, the DD240 for the golf course west bores, and a Ditch Witch JT100 for the golf course east bores.
This strategic deployment allowed the team to maximize equipment suitability. Additionally, it reduced unnecessary relocations between phases.
Ground Conditions & Tooling
Crews encountered a combination of clay and sandstone formations, with harder bedrock zones notably present under the lake. Mud motors paired with tungsten carbide insert (TCI) and mill tooth rock reamers were used throughout. Interestingly, mill tooth tools outperformed expectations in the mixed formation. They became the preferred choice across multiple crossings.
The team operated under an engineered drilling fluid program. However, consistent adaptation was required due to the highly variable formations and the reactivity of native soils with specific mud systems.
Real-time adjustments to viscosity, gel strengths, and additives were critical to maintain bore stability and minimize fluid loss.
Tracking and Accuracy
Precision was essential due to nearby infrastructure, including a major fibre-optic line. Guidance systems included company-owned wireless EM tooling with DC surface tracking and DCI DigiTrak Falcon F5 walkover systems for the JT100 segment. As-built surveys were recorded and submitted after each pilot bore to verify alignment and compliance.
Environmental and Community Constraints
To reduce disruption in the high-density lakefront zone, the team erected sound mitigation walls just 14 m from residential homes. Wood matting was used throughout to minimize site impact. A noteworthy design revision preserved a golf course tee box from demolition and reconstruction. This reflected the project team’s sensitivity to surrounding stakeholders.
Lessons Learned
The Clearwater project highlights the importance of early contractor involvement in trenchless delivery.
EnviroBore worked with the design and construction teams over a year in advance. They conducted field walks, adjusted alignment geometry, and shifted entry/exit points to suit real-world constraints.
This proactive model helped avoid costly rework and optimized success in a space-limited, environmentally sensitive area.
Tyler S. Calvert is vice president of operations and technical services and Justin Hedemann is vice president of EnviroBore Directional Drilling.