Tech Forum: Maintenance Practices for Guided Boring System Operation and Storage
Go longer, larger, and safer in a productive manner is the common mantra for every guided boring contractor. Skill and the right equipment will help you reach this goal, but just as important is the practice of consistent maintenance.
Your crew is most productive when equipment is maintained so projects are completed without delays.
This time of the year Northern America is typically experiencing colder temperatures likely taking your equipment out of service for several months, which presents an ideal time to winterize.
The following recommendations provide a summary of important tips. Contractors should refer to the maintenance and storage sections of their equipment’s operators manual for specific, step-by-step instructions.
RELATED: Tech Forum: Four Steps to Troubleshoot a Challenging Locate
General Guidelines for All Guided Boring Equipment
Before each launch, all the main components must be tested to ensure correct functioning. Also, bring all fluid levels to full.
An obvious and easy maintenance ritual that is often overlooked is to wash all components after each project. If crew members can’t read gauges, check thread connections or see safety decals properly, the risk of an unsafe situation or failure can significantly increase.
Quite a few maintenance issues can be addressed with a simple visual inspection to know when to replace worn and damaged parts. Keep a list of commonly used spare parts, particularly o-rings and filters, and keep them in your power pack. Repaint equipment before long periods of storage. When possible, store your equipment under cover in a well-ventilated area.
Common Guided Boring System Maintenance and Storage Guidelines
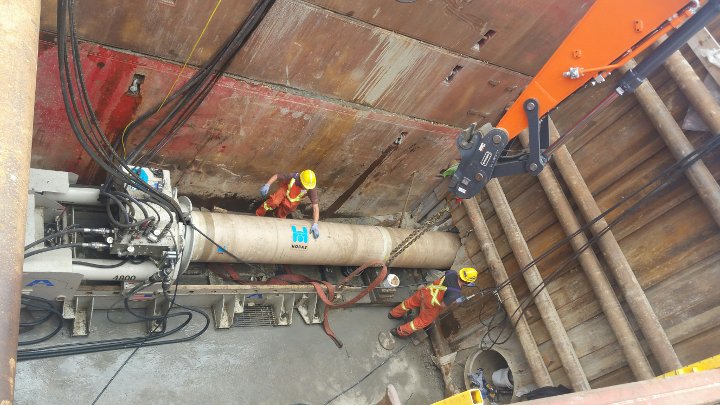
One of the most fundamental pieces of any guided boring system is the pilot tube inventory. A solid practice of cleaning pilot tubes at the end of each project, before fluids have a chance to solidify will ensure that they are prepared for the next drive. Pilot tube maintenance includes a visual inspection and washing the exterior and interior with high-pressure water. Thread wear, caused by side loading and high torque can occur at the thread connections. If thread wear is discovered, it’s important to either rotate the tube or obsolete it from your inventory. Thoroughly dry the tube to prevent rusting and to maintain visibility of the target. Replace o-rings as needed, and apply anti-seize lubricant to the threads and replace the pilot tube caps and plugs if used. In general, a good practice for GBM operators is to assume rack rotation to distribute wear equally throughout the entire inventory.
Check the GBM guidance system theodolite for grade accuracy. Check for cord condition and replace as needed. Guidance systems contain many sensitive elements like the camera and theodolite and must be kept clean and dry. Wipe down all components before returning them to their protective cases. Fisher recommends checking the theodolite’s calibration on an annual basis.
RELATED: Trenchless Technology Tech Forum: Pipe Jacking
The guided boring jacking frame connects to the power pack by way of hydraulic quick disconnects which should be clean prior to connecting them to the jacking frame. Before each drive, grease all lubrication points including the drive adapter swivel. At the completion of the project, disconnect the hosing, replace the caps and plugs and store them inside the power pack. During cold weather operation and prior to storage, blow out the drive adapter swivel and hub assembly with compressed air or flush it with propylene glycol, rated to -50°F. Retract all hydraulic cylinders to prevent corrosion and potential damage to exposed cylinder rods.
Before using the power pack check all fluid levels and add to them as necessary. Check the hydraulic filter indicator to ensure that it is within operating range. Maintain engine oil change intervals per your manufacturer’s recommendations. Before storage in cold climates, drain fluids to prevent freezing and saturate the lines with propylene glycol. Remove all hydraulic hoses and store them indoors to minimize UV damage and maintain a consistent ambient temperature. Add fuel stabilizer to a full fuel tank. Fully charge all batteries. If the plan is to store an engine for over six months, refer to the engine manual for extended storage.
Upsizing tooling increases the bore diameter from pilot tube to final diameter pipe and requires the same level of attention when it comes to maintenance and storage. Clean casing and augers prior to returning them to storage. On larger diameter upsizing tooling, flush all water passages and ports at the end of each drive. Inspect the cutter head tooling and replace worn items. Apply fresh lubrication to all grease points. Keep all tooling pockets free from water that could freeze during storage.
Daily maintenance items on lubrication pumps are to check engine oil, inspect the tank for cleanliness and clean the suction strainer. Drain and clean all tanks and lines at the end of each project. For use in cold weather, flush the pump and lines with propylene glycol.
When operators get in the habit of practicing maintenance intervals and knowing how to properly store guided boring equipment, everyone benefits.